Retina Scan- A Quick Overview
Biometric traits such as fingerprints, facial features, iris & retina patterns, voice patterns, and palm scans are unique to every person. Individuals can be identified accurately by employing these unique characteristics. Many sectors globally employ biometric authentication technology for smooth and accurate identity verification. Retina scan and iris scan, commonly referred to as ‘ocular-based identification technologies’ are the ultimate choices for the authentication of individuals due to the uniqueness of their patterns.
The retina is the posterior portion of the human eye containing intricate networks of vein patterns, frequently called the neural part of the eye. Each retina has a distinctive pattern due to the complex and intricate network of capillaries supplying blood to the retinal part of the human eye. Even the retina patterns of both eyes are unique to each other due to the complicated and enigmatic network of blood vessels.
Difference between Retina Recognition & Iris Recognition
Iris is the colored portion of the eye surrounding the pupil, also known as a kaleidoscope of colors and patterns. This colored part of the eye generally contains three types of iris patterns including pigmented rings, furrows, and crypts, rendering it unique to each individual.
Both retina and iris patterns are ocular-based ID verification methods, however, they are unique in their working mechanism and authentication approach. Iris Recognition uses a digital camera to capture the image and find the match. In this recognition, the optimal distance between the eyes and the camera is 3-10 inches. On the other hand, retina recognition uses a retinal scanner which sends a beam of light into the human eye to accurately retina patterns and collect them for verification purposes. The patterns of the retina remain almost the same throughout life unless any disease appears, compared to iris textures that are contemplated to never change in the whole life.
How Accurate Retina Recognition is?
Retina patterns are foolproof, as it is daunting to replicate these intricate networks of blood vessels. With a false acceptance rate of 0.0001%, retina scan comes forth as the most accurate biometric trait and serves as a gateway to the future of ID verification. Retina recognition is deemed highly accurate as the error rate in identifying individuals is one in a million.
Retina recognition is much better than other types of biometric modalities, as retina patterns are 70 times more accurate than iris patterns, and 2,000 times more secure than fingerprint scans.
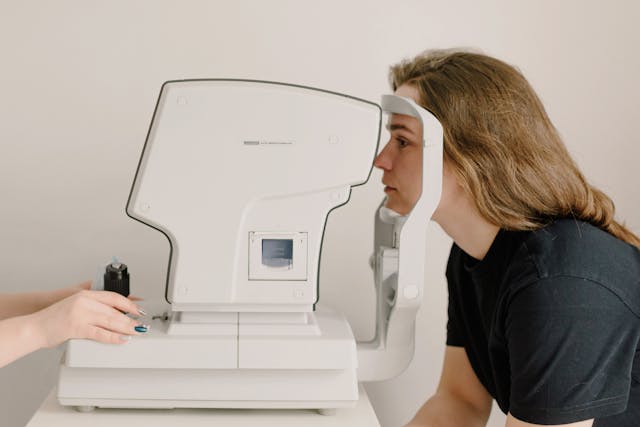
Exploring the Operating Mechanism of Retina Scanner
The working of retina scanning is dependent on the unique network of blood vessels supplying blood and nutrients to the retina. The retina patterns are captured through retinal scanners, which direct a beam of infrared light into the retina. The subtle ray of light is kept at an adjacent position and sometimes goes unnoticed. The scanners and eyes are kept at an optimal distance that is 3-10 inches for accurate capturing to avoid any inconsistency.
The beam of light is absorbed by the blood vessels present in the retina, which gets more visible after light absorption and facilitates capturing the patterns smoothly. During the whole process of pattern acquisition, the eyes must be motionless, with no blinking or glancing for better focus. Once the image is captured, retinal scanner software merges all the details and constructs a minute template which is then stored and utilized for ID verification.
Is Retina Scan the Ideal Choice for ID Verification?
To ensure the integrity of security and fight the rising threats of identity theft, organizations must develop robust measures. Biometric authentication methods prove to be promising in this context and offer numerous benefits to industries employing these sophisticated and unique traits. Of all biometrics, retina scans are rendered as the most accurate owing to their unparalleled stability and uniqueness.
A detailed study on retina scanning reveals that retina patterns remain unchanged throughout the lifetime contrary to fingerprints and facial features which fade away with time. This astonishing feature makes retina scan the most accurate and security biometric identifier.
Which Industries are Using Retina Recognition for Verification
Retina recognition is transforming the identity verification process across various industries globally from public to private sectors. Numerous sectors including law enforcement, healthcare, financial institutions, telecommunication, military, and defense are integrating retina recognition in their systems to ensure effective and error-free authentication of individuals.
- Law enforcement and police departments employ retina scanning to keep an eye on potential individuals and deter any unauthorized entry into the system.
- Banks and FIs are known to use retina recognition to ensure secure financial transactions, particularly in customer onboarding to effectively know who the customers are and spot risky incidents.
- Healthcare sectors potentially leverage this ocular-based authentication method to ensure medical services are delivered to the right persons and to tackle medical identity fraud.
Conclusion
Retina recognition offers numerous benefits in various industries globally, as ID verification through retina scanning is quick and requires less time to authenticate individuals. As the retinal patterns are securely located inside the eye, it’s not prone to any external damage or environmental changes, rendering it a trustworthy biometric identifier in today’s fast-paced world. However, the cost and complexity associated with the utilization of retinal scanners are limited and less adopted. Additionally, the technology is less applicable to the public, as eyes are sensitive to light exposure. Despite that, the right balance between responsible implementation and managing cost issues can promise a better world of retina recognition.

Sumana Das